Adult chickenpox
OVERVIEW
What kind of disease is chickenpox?
Chickenpox is a highly contagious rash-causing disease. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and is typically transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or exposure to their respiratory droplets. The disease most commonly affects children aged 2 to 10.
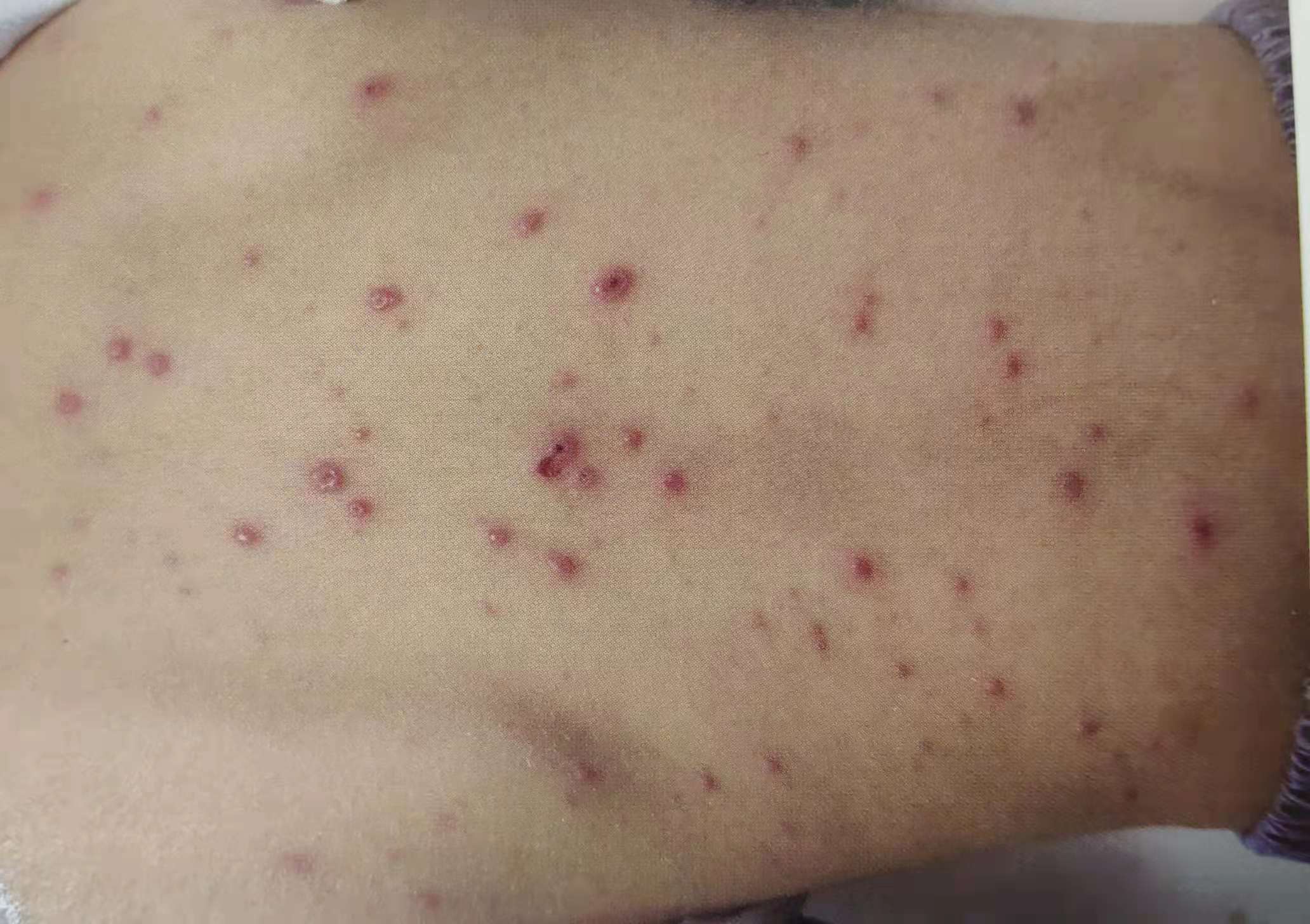
Is chickenpox common in adults?
Chickenpox in adults is now quite common, but the disease is most frequently seen in children.
What are the differences between adult and childhood chickenpox?
-
In children, chickenpox symptoms are usually mild. Early signs include fever, loss of appetite, and lethargy. Within 1–2 days, a rash appears all over the body, and the blisters crust over after a few days.
-
In adults, chickenpox symptoms are more severe, with a longer prodromal period, high fever (>38.5°C) lasting 3–5 days or longer, and more pronounced systemic symptoms such as dizziness, headache, muscle pain, and fatigue. Complications like varicella pneumonia or varicella encephalitis are also more common. Most patients recover well, but some adults and a few children may have a poorer prognosis.
SYMPTOMS
What does chickenpox look like?
Chickenpox initially appears as a red rash, which turns into small oval-shaped water blisters with a red halo within hours. After a few days, the blisters rupture and scab over, while new blisters continue to appear. As a result, intact blisters, ruptured blisters, and scabs can often be seen simultaneously on a patient's skin. Some patients may also develop ulcers in the mouth or on the external genitalia.
Where does chickenpox usually occur? Is there a sequence to the affected areas?
-
It most commonly appears on the trunk, face, and neck, with the trunk being the primary site. Typical chickenpox shows a centripetal distribution (most on the trunk, decreasing toward the periphery).
-
There is a sequence—chickenpox first appears on the trunk and then spreads to the face and limbs, with hands and feet being less common.
What are the symptoms of chickenpox in adults?
In adults, chickenpox symptoms are more severe than in children. During the prodromal phase, fever may be high (>38.5°C) and last for 3–5 days or even longer, accompanied by systemic symptoms such as dizziness, headache, muscle pain, and fatigue. A large number of rashes may appear within 1–2 days, appearing bright red with numerous blisters that are more prone to rupture. The trunk, face, and neck are the most commonly affected areas.
What serious complications can chickenpox cause in adults?
-
Varicella pneumonia: Mild cases may only present with slight coughing, while severe cases may involve high fever, chills, chest pain, coughing up blood, and difficulty breathing. Abnormalities can be detected through chest auscultation and X-ray. Most patients recover within 1–2 weeks, but a very small number may die from respiratory failure.
-
Varicella encephalitis: Symptoms may include dizziness, headache, vomiting, drowsiness, high fever, convulsions, unsteady gait, and slurred speech. About 80% of patients recover completely with treatment, and its clinical manifestations are similar to viral encephalitis.
-
Secondary infections: If the rash covers a large area and personal hygiene is poor or anti-infection treatment is neglected, secondary skin infections may occur. Severe cases can lead to skin gangrene, sepsis, or septicemia.
CAUSES
Why do adults get chickenpox?
Adults who have not been exposed to the varicella-zoster virus (those who did not have chickenpox as children) may experience weakened immunity due to factors such as high stress, poor sleep, staying up late, or irregular eating habits. If they happen to be around someone with chickenpox or come into contact with an infected person during this period, they are highly susceptible to contracting the virus and developing chickenpox.
If an adult who never had chickenpox as a child is infected with the varicella-zoster virus, will they get chickenpox or shingles?
There are two scenarios for those who did not have chickenpox as children:
-
First, if they were never infected with the virus, the initial infection in adulthood will result in chickenpox.
-
Second, they may have been infected with the varicella-zoster virus but did not develop symptoms or had atypical manifestations that went unnoticed. In this case, the virus can remain dormant in the body and later reactivate due to triggers (such as fatigue or poor sleep), leading to shingles.
Is adult chickenpox contagious? How is it transmitted?
Yes, it is contagious. It is typically spread through respiratory droplets or direct contact with an infected person.
DIAGNOSIS
Suspected Chickenpox: What Tests Are Needed?
If you suspect you have chickenpox, the best approach is to visit a dermatology or infectious disease department at a reputable hospital. Based on the patient's condition, tests such as a complete blood count (CBC), varicella-zoster virus (VZV) antibody test, vesicle fluid culture, VZV antigen test, or PCR may be performed for diagnosis.
Why Are CBC, VZV Antigen, or Antibody Tests Necessary? What Should Be Noted?
Since chickenpox is caused by a viral infection, a CBC can help determine whether the blood profile aligns with a viral infection. Meanwhile, VZV antigen and antibody tests can confirm the presence of the virus in the vesicle fluid, aiding in diagnosis.
Antibody testing is best performed 7–10 days after the rash appears. The other tests have no special requirements and can be conducted as soon as symptoms appear.
What Diseases Can Adult Chickenpox Be Confused With? How to Differentiate?
Adult chickenpox can be easily confused with papular urticaria or impetigo.
-
Papular Urticaria: Typically caused by insect bites, the rash consists of edematous red papules, sometimes with small blisters at the center. The mouth and scalp are usually unaffected, and itching is intense.
-
Impetigo: Commonly occurs on exposed areas like the face and limbs. The rash starts as blisters, then develops into yellow pustules with thick, honey-colored crusts. A CBC would indicate a bacterial infection.
What Is the Difference Between Adult Chickenpox and Shingles?
These are two distinct conditions caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Initial infection leads to chickenpox, after which the virus remains dormant in the body. Reactivation due to fatigue or weakened immunity results in shingles.
-
Chickenpox: The main rash consists of small blisters surrounded by redness, which later rupture and scab. The rash is diffuse, predominantly affecting the chest, back, face, and neck.
-
Shingles: Presents as band-like, clustered red patches and blisters, usually on one side of the body, and may be accompanied by burning pain or other neurological symptoms.
TREATMENT
Which department should adults with chickenpox visit?
Generally, you should go to a local infectious disease hospital. If there is no specialized infectious disease hospital, you can also visit the infectious disease department or dermatology department at a regular local hospital.
Do adults with chickenpox need treatment? Can it heal on its own? How long does it take to recover?
Adults with chickenpox usually experience more severe symptoms than children, so it is recommended to seek treatment at a regular hospital. The treatment plan should be tailored to the patient's condition. Self-treatment at home is not advised. The disease typically lasts about 2–3 weeks, so recovery usually takes 2–3 weeks.
What are the treatment options for adult chickenpox? Is hospitalization necessary?
-
First, isolate as early as possible until all rashes have crusted over.
-
Depending on the patient's condition, oral or intravenous antiviral medications such as acyclovir or valacyclovir may be prescribed.
-
Symptomatic treatment is also required. For fever, antipyretics like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be used. For skin itching, oral antihistamines such as cetirizine or loratadine may be given, and calamine lotion can be applied topically.
-
If the rash ruptures, antibiotic ointments can be applied to prevent infection.
-
If severe complications such as viral encephalitis or viral pneumonia occur, antibiotics or other appropriate medications should be used based on the patient's condition.
-
Since chickenpox is contagious, whether hospitalization is needed depends on the severity of the condition.
What should pregnant women do if they get chickenpox? Is termination of pregnancy necessary?
If chickenpox occurs within the first 20 weeks of pregnancy, it may lead to premature birth, fetal malformations, or stillbirth. Therefore, pregnant women with chickenpox should immediately seek prenatal counseling at a maternity hospital or gynecology department to determine whether termination of pregnancy is necessary.
What should breastfeeding mothers do if they get chickenpox? Should they stop breastfeeding?
Adult chickenpox symptoms are severe and highly contagious. Breastfeeding mothers with chickenpox should immediately isolate themselves from the child, stop breastfeeding, and seek treatment at a regular hospital.
Will adult chickenpox leave scars or cause sequelae?
Generally, no scars will remain. However, if blisters rupture and become infected or are scratched, scarring may occur.
Most patients with uncomplicated chickenpox recover well without long-term effects.
What is the prognosis for adult chickenpox?
With proper treatment, uncomplicated chickenpox will gradually heal as the rashes crust over and fall off, and no follow-up is needed. However, if complications arise, follow-up visits should be scheduled as directed by the doctor. Severe adult chickenpox or delayed treatment leading to complications may result in adverse outcomes.
Additionally, individuals with immune abnormalities or severely compromised immune systems, such as AIDS or cancer patients, may have a risk of recurrence.
DIET & LIFESTYLE
What should adults with chickenpox pay attention to in their diet?
-
Eat easily digestible foods and maintain a balanced diet;
-
Avoid spicy or irritating foods and drink plenty of water;
-
Eat more fresh vegetables and fruits;
-
Consume moderate amounts of protein-rich foods like eggs and fish to boost immunity.
What should adults with chickenpox pay attention to in daily life?
-
Maintain a regular schedule, avoid overexertion and staying up late, and rest in bed during the illness;
-
Isolate after onset, and both the patient and family members should wear masks to prevent transmission;
-
Disinfect贴身衣物 by boiling or sun exposure, and ensure daily room ventilation.
How long after recovering from chickenpox can an adult get pregnant?
It is recommended to wait at least 3–6 months to prevent potential harm to the fetus from the virus or antiviral medications. Consult an obstetrician for prenatal advice if necessary.
PREVENTION
How to prevent chickenpox in adults?
-
You can get the live attenuated varicella vaccine at a vaccination center, which is about 90% effective in preventing chickenpox;
-
If there are chickenpox patients around, be sure to isolate, wear a mask, and wash hands frequently;
-
Maintain a regular routine, avoid staying up late or excessive anxiety, eat a balanced diet, ensure adequate sleep, and exercise more.
How can adults with chickenpox prevent infecting others?
Since chickenpox is transmitted through respiratory routes, infected individuals should isolate themselves from others. Both the patient and family members should wear masks, and personal clothing, bed sheets, and covers should be washed and disinfected with hot water to effectively prevent transmission.